原始题目:剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制 (opens new window)
# 方法一:哈希表
遍历链表,根据就节点 ,创建新节点 ,然后使用哈希表保存新旧节点的映射关系 。在遍历一次原始链表,当遍历到每个节点时,执行以下操作
- 根据 从哈希表中拿到对应的 ,拼接到新链表中。
- 根据 从哈希表中拿到 对应的 指针应该指向的节点。
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 用哈希表先建立每个旧节点与新节点的映射
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
Node newCur = map.get(cur);
// 找新节点的 next 和 random,它们都应该在 map 中
// 且各自与 cur.next 和 cur.random 对应
newCur.next = map.get(cur.next);
newCur.random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: 为链表的节点个数。哈希表的插入与搜索都是 时间的,链表的拼接也是 的。
- 空间复杂度: 为链表的节点个数。哈希表需要存储全部的节点。
# 方法二:拼接+拆分
拼接
先把新旧链表连接在同一个链表上,或者可以理解为在旧的节点后面跟着一个新的节点,新结点值等于旧的结点值,如下图中的第 步。然后遍历拼接后的链表,找到新节点的 指针,如下图中的第 步
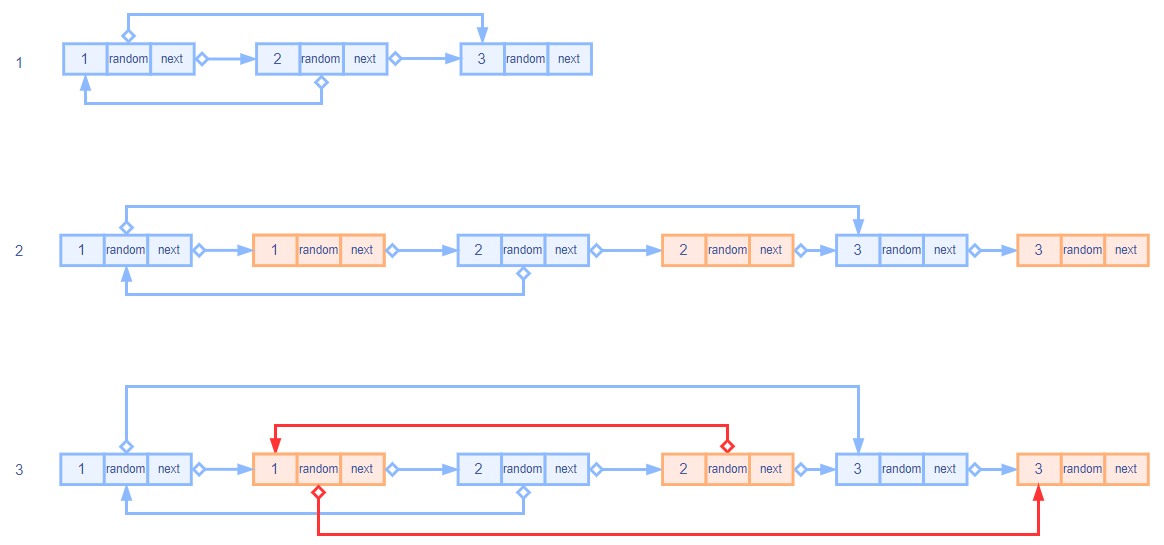
拆分
然后遍历拼接后的链表,进行拆分操作。使用双指针, 指针指向 , 作为 的前驱节点指向 。接下来就是 和 的 指针都是两步走, 。直到 指针走到尾部,就结束了。
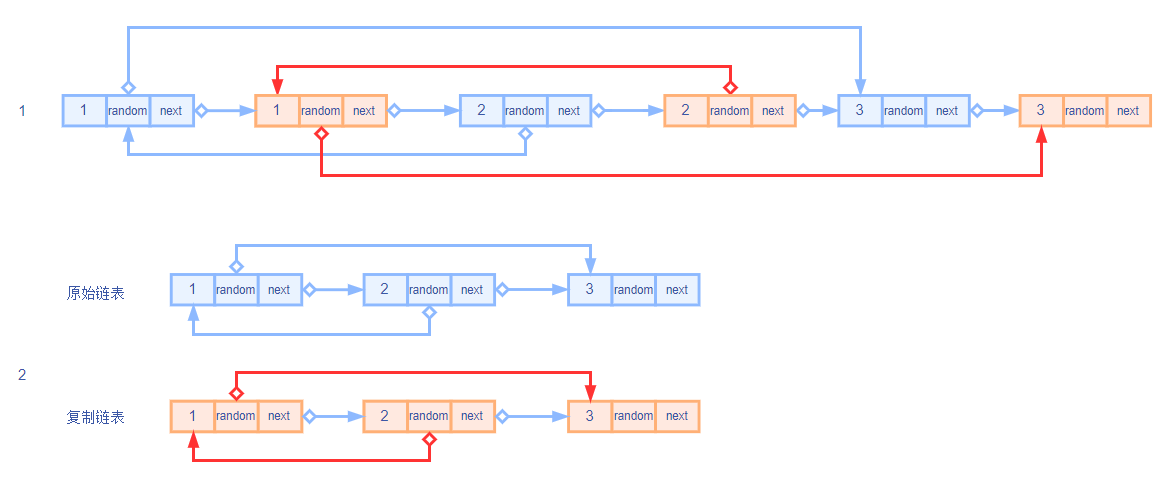
代码:
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
// 先把新旧链表连接在同一个链表上
// 或者可以理解为在旧的节点后面跟着一个新的节点,新结点值等于旧的结点值
// 比如:
// 1->2->3
// 1->1->2->2->3->3
while (cur != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(cur.val);
newNode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = newNode;
cur = newNode.next;
}
cur = head;
// 找到新节点的 random 节点
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.random != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 拆分链表
cur = head.next;
Node ans = head.next;
Node pre = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 处理原链表的尾结点
pre.next = null;
return ans;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: 为链表的节点数目,算法中需要进行三次链表遍历,每一次占用 时间,循环中的操作占用 时间。
- 空间复杂度:算法中使用的变量据占用 空间。
